Skin Donation

Senior Resident (Mch)
Assistant Professor
Professor & Head of Department (Corresponding Author)
Skin is one of the largest organs of body, and functions to regulate temperature, sensation, and vitamin D metabolism. It provides a physical barrier to the mechanical, chemical and microbiological insults of the environment. The old proverb still signifies that “A man can live with half liver and one kidney, but when skin is lost, it is difficult to survive”.
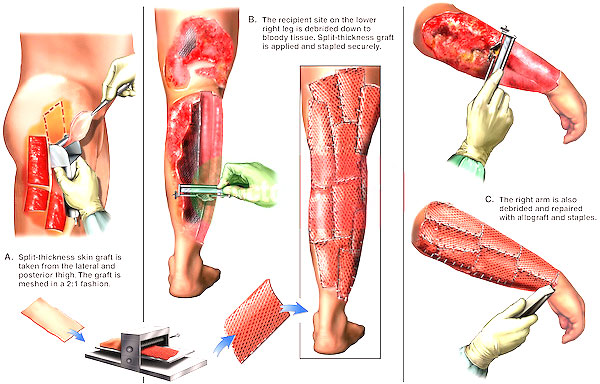
The skin is lost and needs replacement when a large area of body is burnt or traumatized. The problem is so severe that more than 70 lakh people sustain burns every year in India, with more than with over 7 lakh of these patients requiring hospitalization. Almost half of these patients succumb to death and one third are left with complications including post burn contractures that require multiple subsequent operations. It is known that early grafting leads to lower rates of infection and subsequent complications. Autograft (skin taken from same individual) and allograft/homograft (skin taken from cadavers/relatives/other human beings) are two common sources of grafts. Although autograft represents the gold standard given the autologous nature of the tissues, allograft/homograft is needed for large burns in patients with limited donor sites. Skin donation in the form of homograft/allograft etc is important in order to be able to perform rapid wound coverage among patients with severe total body surface area burns. In this manner, skin banks can reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with such injuries. The article will provide information about skin donation and skin banking in order to improve awareness about skin donation. There are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Who can donate skin?
Any volunteer, dead or alive, can donate his/her skin. A doctor from skin bank usually goes to home of dead person, harvests the skin within 6-8 hours using aseptic technique, dresses the wounds, and returns the dead body to relatives. In case of death in hospital, the process of retrieval of skin becomes easier if relatives volunteer to donate the skin to skin bank. Signed consent from appropriate relatives are required before harvesting the skin. Any individuals from age of 12- 60 years can donate the skin. Contraindications to donation include individuals with history of hepatitis, jaundice, skin diseases, veneral disease and cancer.
How do skin bank screen for transmission of infection or disease by donor skin graft?
Blood samples taken from donors are tested for HIV 1& 2, Hepatitis B & C and syphyllis serologically. Microbiological testing for staphylococcus, streptococcus and pseudomonas organisms are also performed. Any skin tissue having more than 105 organisms/gm of tissue is not suitable for use and is discarded.
How do skin bank store the skin?
There are various methods of storage. Refrigeration, Deep freezing and Lyophilazation are main methods utilized.
Refrigeration is the most common form of storage utilized. In this method, the graft is wrapped in a Vaseline/saline moistened gauze, and stored at 4 degrees centigrade in a sterile bottle. In this method, the graft can be stored for 3 weeks. Although viability of graft decreases with time, nutrient enhanced medium can be used to increase survival.
Deep freezing or cryo-preservation is a method that involves cooling of the skin graft to ultra low temperatures by using liquid nitrogen ( -80 to -196 degrees) after pretreatment with cryo-protecting agents like Glycerol and Ethylene glycol. Grafts cooled to -80 degree can be stored for 6 months, while those cooled to196 degree can be stored indefinitely.
Freeze drying is the process during which the graft is first cooled and water is removed by sublimation. The tissue is vacuum sealed, and subsequently sterilized by gamma radiation.
Who are the recipients for using skin bank?
Any hospital/doctor caring for burn or trauma patients.
Does the cadaver skin graft permanently take to the recipient area of patients?
No, cadaver skin graft does not stick to the raw areas caused by burn or trauma permanently. After 4 weeks, it starts separating from wound and needs to be replaced with autologous tissue. Importantly, however, cadaveric skin improves the potential for immediate wound coverage which directly affects morbidity (decreases pain) and mortality ( by decreasing infection ) .
What may be the harmful effect to the patients who receives skin graft from cadaver?
Harmful side effects are minimum. There is a little risk of infection and acute rejection.
What is the future of skin donation in India?
Skin donation is becoming increasingly important in the care of burn and trauma patients. Every individual should volunteer to donate his/her skin after death. It is service to humanity. The awareness must spread among school children, NGOs, and citizens of the country. We must take part in saving someone’s life by donating our skin. ‘Donate skin, save life’ is an important slogan required to increase awareness about the importance of skin donation.

